Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and allows glucose to enter the body's cells to provide energy.
There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This type of diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form and is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity and lack of physical activity. In this type, the body becomes resistant to insulin, and the pancreas cannot produce enough to compensate. It is typically diagnosed in adults, but due to the rising rates of childhood obesity, it is increasingly being diagnosed in children as well.
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth. However, women who have had gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
The symptoms of diabetes can vary but often include increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision. If left untreated, diabetes can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems.
Managing diabetes involves maintaining healthy blood sugar levels through a combination of medication, diet, and exercise. People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin injections or use an insulin pump to control their blood sugar levels. Those with type 2 diabetes may manage their condition with oral medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes insulin injections.
A healthy diet for diabetes includes consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods in appropriate portions. This typically involves limiting the intake of sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats while emphasizing whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
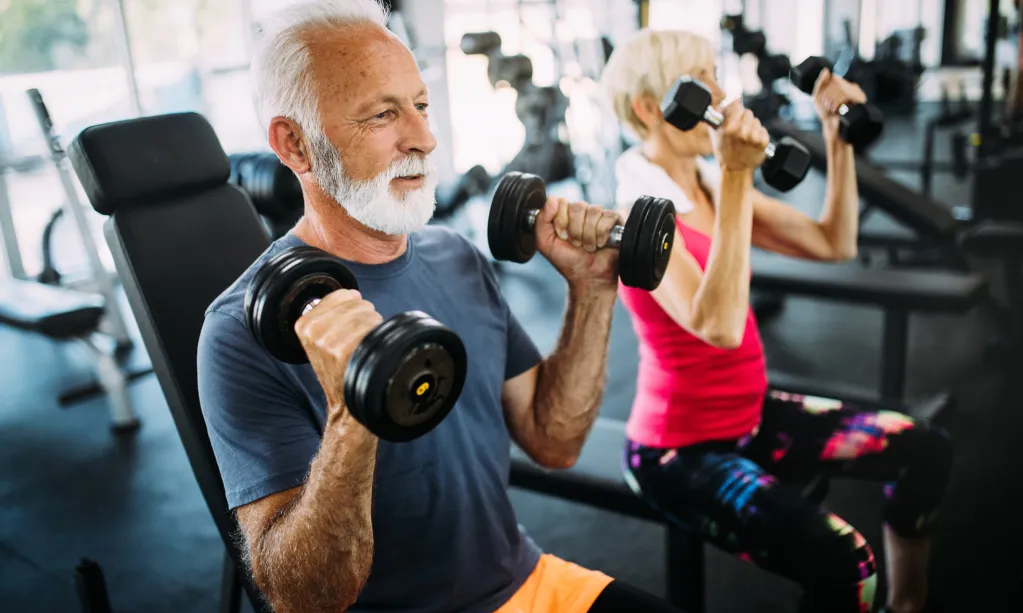
Regular physical activity is also important for managing diabetes. Exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and maintain a healthy weight. It is recommended to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with strength training exercises.
In conclusion, diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels. It is important to understand the different types of diabetes, their symptoms, and how to manage the condition through medication, diet, and exercise. With proper management, people with diabetes can live healthy and fulfilling lives.
ADS








